In the last post, I discussed why unreliable narrators are such compelling storytellers and why I feel they are more worthy of study than ever before in this epistemically challenged social media age. If you’re interested in how the 2015 video game Her Story is an excellent close reading challenge, and why I was inspired to teach it as a text, go back and check that out. In this second post, we will be looking at how and why I built this unit on unreliable narrators around a series of short stories that work their way up to Her Story.
Can I get that in writing?
As an English teacher, I have a writing bias. Communication – especially in written form – is as essential as it has ever been, even more so in the Internet age. I tell my students all the time that they are almost guaranteed to be making their first impressions with someone via their writing, whether it’s a social media post, a resume, an email, or published online content. As a result, whenever I build a unit – whether traditional or game based – the first question I ask myself is, “How can I get them to write about this?”
But before we write, we must read.
While there are some fantastic unreliable narrators in novels (like Chief Bromden, Underground Man, Nick Carraway) and films (Verbal Kint, Tyler Durden, Lenny), short stories provide a balance and variety that English teachers often find particularly useful in lesson planning. Focusing on shorter narratives also allowed me to utilize a key pedagogical method video games have used for a long time: scaling difficulty. By studying multiple, shorter narrators, I could introduce my students to gradually more complex narratives and plots. But where to begin?
Research into the teaching of unreliable narrators brought me to a work by Michael W. Smith on teaching unreliable narrators. That was an invaluable starting point for me as he breaks down a lot of the more complex literary theory into understandable chunks, and he also had the same idea as me to introduce different narrators using short stories.
But an unreliable narrator is not just the disembodied voice of the author, or even just a character within the story. They are an opponent. And that will require some additional tools with which to spar.
Mindhunting
To help my students in their “investigation” of each unreliable narrator, I drew up a graphic organizer so they can scaffold the process. Here is what it looks like:
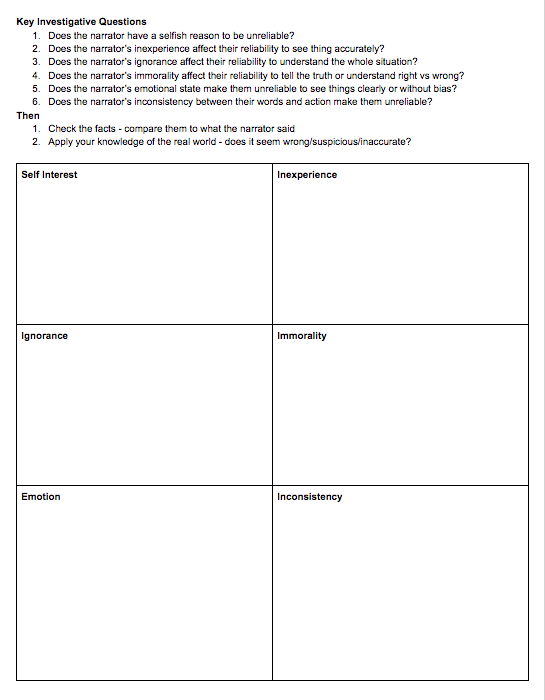
The second page includes space for them to summarize and analyze the important facts of the story and utilize their real world knowledge to evaluate the reliability of the narrator’s perspective.
Here is a link for download.
The most important part of any investigation is gathering evidence. As master gentleman detective Sherlock Holmes opined in The Scandal in Bohemia:
It is a capital mistake to theorize before one has data. Insensibly one begins to twist facts to suit theories, instead of theories to suit facts.
Especially when your source of evidence could be purposefully manipulative, having an accessible record of the most important facts to cross reference, compare, and contrast is going to be essential. It was not surprising to me that this task of textual annotation was conducted with far more engagement and effort by my students. This was even from students who would normally complain about annotation because it “disrupted” their reading and they just wanted to “enjoy the story”. And we hadn’t even made it to the video game yet!
This is a great example of the benefit of game based learning. When you contextualize an activity with greater meaning, it becomes far more enjoyable and less onerous. An activity without meaningful context is drudgery, and that’s a category that defines far too much traditional schoolwork.
This table was the focus of their homework as we read each story. And when we played Her Story, it would be their main form of daily work, investigation, and note taking. The completed chart for Her Story was collected and graded, while the others were checked for completion and used for class discussion.
Now that they had their interrogative tools, it was time to work our way up to the Final Boss, Her Story‘s Hannah. But before you can get to the Final Boss, all gamers know they will have to face a series of increasingly difficult “mini-bosses“. The mini-boss is a reliable pedagogical trope in video games. They function as “skill checks” to insure the player has the requisite abilities to continue into the next phase of the game, and may even force players to master a specific technique that will be necessary to progress.
I endeavored to incorporate that mechanic into the unit itself by framing the progressively complex stories as “mini-bosses” to prepare the students for Her Story. They would need to acquire certain close reading and analytical skills before they could effectively tackle the multi-media challenge of the game.
Spoiler alert: if you want to read all these stories first, here they are! If you have already read them/don’t care, read on!
The Cask of Amontillado by Edgar Allan Poe
The Yellow Wallpaper by Charlotte Perkins Gilman
In a Grove by Ryūnosuke Akutagawa
Level 1: The Obvious Unreliable Narrator

This is the “Easy Mode” of unreliable narrators. We have a clueless parent being duped, over and over, by her mischievous and masterly mendacious son. What’s interesting about this story is we actually have two unreliable narrators: Laurie, the son, and the unnamed mother who narrates the story itself. Laurie is a more direct unreliable narrator: he spins elaborate tales of his various kindergarten crimes and pins them on the imaginary “Charles”. He is unreliable in the most understandable sense: he lies to stay out of trouble and everything “Charles” did, he did. As a directly dishonest narrator, the truth is easy to discern, and is laid out pretty clearly (especially upon a second reading) by the story’s twist ending. For students, his motivations are familiar as well. We’ve all fibbed (or been tempted to fib) to our parents to deflect, hide from, and mitigate the consequences for our bad decisions.
However, the mother is the primary unreliable narrator and her unreliability contrasts well with her son’s. The mother’s unreliability comes not from dishonesty, like Laurie’s, but from naïveté and from being “love dumb”, as my friend would say. She can’t possibly imagine that her “angelic” child could be such a terror at school; the father (who reminds me of Mike’s dad in Stranger Things) is equally clueless as he sips his coffee and reads the newspaper. We tend to believe what we want to believe even when there’s plenty of evidence to the contrary. Who assumes their five year old has mastered manipulation?
This is a useful introduction to the variety of unreliability. A narrator can be unreliable without even knowing they are unreliable! How often have you forwarded or shared something before checking your facts? The research indicates the answer for most people, most of the time is “a lot”. This story is great fodder for exploring important concepts like confirmation bias with students.
Level 2: The Mastermind

And now we knock things up a notch. This time the narrator is toying with his audience specifically.
The narrator of Edgar Allan Poe’s famous short story is playing a game with the reader. He acknowledges his audience – “You, who so well know the nature of my soul” – in a way few first person narrators do, and identifying the audience is a key interpretive choice. Is it a priest? Is he confessing because he feels guilty for the murder of Fortunato, or is he simply executing the last step of his meticulously planned revenge? He states very clearly that true revenge cannot end with punishment for the avenger, so is this narrative a deathbed confession to cleanse his soul and avoid divine punishment? Is this a final lesson in revenge, a case study for the younger Montresors to learn from and emulate as their family motto – Nemo me impune lacessit – demands? Or perhaps, this is simply the deluded ravings of a madman.
This interpretive fulcrum requires a great deal of empathy from the reader; to “beat” this narrator they have to be able to construct a motive for the confession because Montresor immediately reveals himself as unreliable when he avoids naming the reason for his gruesome revenge against Fortunato. What are these mysterious “thousand injuries” and what exactly was this “insult” that forced Montresor to murder his enemy in the worst possible method? And if they are so terrible, why not name them?
This is a great challenge because the students know the narrator is unreliable but they are not given a clear interpretation as to how and why. Insanity? Sadism? Justified, if gruesome, revenge? A monomaniacal urge to commit the perfect crime? A complete interpretation can be constructed but the reader must build one themselves. And they must use empathy, a underappreciated analytical tool. Your opponents must always be understood, perhaps even particularly so.
Level 3: The Chimaera
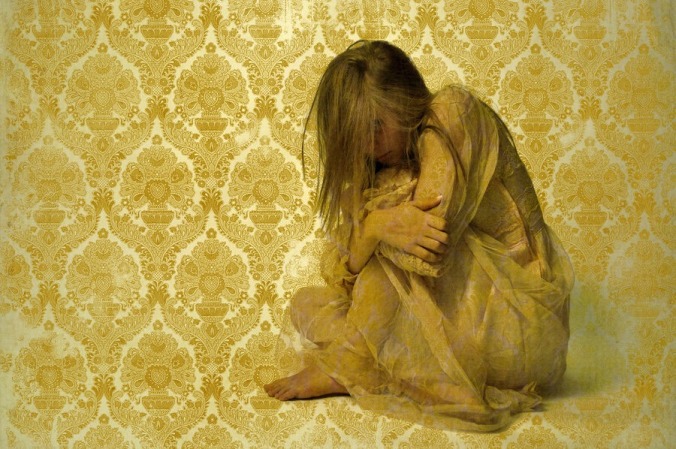

Now our narrator is unreliable but perhaps in ways they are not even aware. The complexity builds when the narrator could pass a polygraph because they don’t know they’re lying.
Enter The Yellow Wallpaper.
This particular opponent takes many forms – a poor soul tortured into delusion, a dangerous lunatic justifying her own imprisonment, a resilient victim fighting the patriarchy, and even a ghost, or perhaps some combination of them all. While Montresor had mysterious motives, even the identity of this narrator can flake and peel under examination like the titular wallpaper that becomes the object of her obsession.
The students have to untangle who the narrator is by her own descriptions and shifting voice. Why are there rings bolted into the walls? Bars on the window? A bed nailed to the floor? Are they really remnants of a nursery for “little children”? Did these “little children” really gouge, splinter and scratch the floors and walls, or is she not the first person of unsound mind to be locked in this room?
But what of the “ghostliness”? The “draught” and horrific wallpaper that seems to immediately entrance and horrify the narrator? What of this skulking woman “trapped” in the wallpaper? A psychotic break or a malevolent spirit of a haunted house? And what of the mysterious final words?
“I’ve got out at last,” said I, ” in spite of you and Jane! And I’ve pulled off most of the paper, so you can’t put me back!”
Who is Jane? If she’s the heretofore unnamed narrator, has the ghost finally escaped from its decorative imprisonment? The students have to untangle the supernatural from the merely deranged and each interpretation beguiles the other.
On top of these myriad interpretative puzzles, however, they must also grapple with the historical context. They have to combine the knowledge of modern psychology (especially about the trauma of isolation) with the biased and uninformed medical practices of the time. Sorting the historical anomalies from the narrative ones requires even more attention to detail and multiple levels of careful interpretation.
Level 4: The Mirror Maze

And now it all goes sideways.
In a Grove, by Ryūnosuke Akutagawa, is probably more well known by its film adaptation, Rashomon. It is an early modernist short story and exemplifies that era’s exploration and skepticism of an objective truth. The story denies all attempts to establish a coherent interpretation. Every suspect for the samurai’s murder not only has the means, motive, and opportunity to commit the crime, but all four suspects insist they are the perpetrator, including the victim (via a medium). Unlike The Yellow Wallpaper, there are no interpretive paths, labyrinthine though they may be, that can be effectively charted. This story challenges the reader to simply embrace the fact that despite our desperate human urge to categorize, organize, and understand, sometimes the chaos just wins and there’s nothing you can do about it.
There is obviously the opportunity to plumb the depths of epistemology and discuss the the Great Questions, of which the answer is 42, but also explore things like apophenia, and why we are so uncomfortable without complete knowledge of the events in our life.
Now that the students have worked their way through a variety of instructional “mini-bosses” it is time for their ultimate challenge, Her Story. I should note that these stories are hardly the only options and a variety of texts could be used to develop a useful “difficulty curve” based on the experience you want to create for your classroom.
The Game is Afoot
And now, time for Hannah. The Sephiroth of Stories, the Ganondorf of Games, the Liquid Snake of Lying. The Final Boss.

In the third post, I explore how I played the game in class using a “hot seat” method, the writing assessments, and student reception of the unit.

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.
Pingback: Completely Unreliable | thealternateclassroom
Pingback: Completely Unreliable: Time to Play | thealternateclassroom